Exploring the Health Risks of THC and How to Use it Safely

When people say “marijuana,” they are usually referring to two species of cannabis plant: Cannabis indica and Cannabis sativa. Both contain many active ingredients, but the two major ones are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). THC is the psychoactive agent in weed that can seriously affect your physical and mental health. Additionally, THC abuse can lead to addiction, especially in young people.
The growing popularity and legalization of medical and recreational marijuana have seemingly resulted in an increase in daily marijuana usage among teenagers. This trend is concerning, especially considering the decreasing awareness among new users about the potential risks associated with cannabis misuse. In this article, we aim to highlight these potential dangers and provide guidance on how to safely use marijuana.
What THC-High Marijuana Does to Your Mind and Body

Lately, we have been hearing a lot about the therapeutic benefits of cannabis, many of which are legitimate. However, let us not forget that even the best medicine can be dangerous when used incorrectly. The ways people use cannabis vary from inhaling smoke to eating cookies, but all of them pose similar risks of developing negative side effects from THC. Doctors divide these side effects into two major groups — short-term and long-term effects of cannabis.
Short-term effects include:
- Feeling high: This altered state of consciousness can result in sensory changes such as brighter colors, enhanced music appreciation, and a heightened sense of relaxation. However, this euphoric state can also lead to disorientation and impaired judgment. This euphoric state may last for about four hours.
- Mood and behavioral changes: Some users may experience unexpected laughter, anxiety, hyperactivity, or lethargy.
- Cognitive impairment: THC can affect your thinking, memory, motor skills, and decision-making abilities. You may feel disoriented, clumsy, and struggle to hold a conversation.
- Cardiovascular effects: THC can cause significant drops in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate, which can lead to fainting, especially when smoking or vaping weed.
- Hallucinations and delusions: High doses of THC can sometimes cause you to perceive things that aren’t there, leading to a distorted sense of reality.
- Physical discomfort: Some users may experience red, dry, itchy eyes, and dry mouth after using THC.
Long-term side effects of cannabis include:
- There is a risk of addiction: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that 10% of people who use weed become addicted. However, the rates are much higher among teenagers, with one in six cannabis users becoming addicted.
- IQ decline: Regular use of weed can in some cases lead to memory impairments and other mental issues, including problems with learning and focus. Cannabis can also distort brain development in children, and those who smoke weed in their early teens may be less successful at school. Cognitive functions do not restore even after they quit pot as adults.
- Marijuana and nausea: Although weed is known to help with appetite and treat vomiting and nausea, regular cannabis use may lead to cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS), which causes people to vomit and feel sick. The mechanisms behind CHS are still unclear, but some theories suggest that marijuana negatively affects the liver or the nausea center in the brain.
- Serious psychiatric problems: Regular cannabis use may also lead to serious psychiatric problems, such as anxiety, suicidal thoughts, psychosis, and even schizophrenia. However, the evidence linking marijuana to such serious mental diseases is limited.
How THC Works in Our Bodies
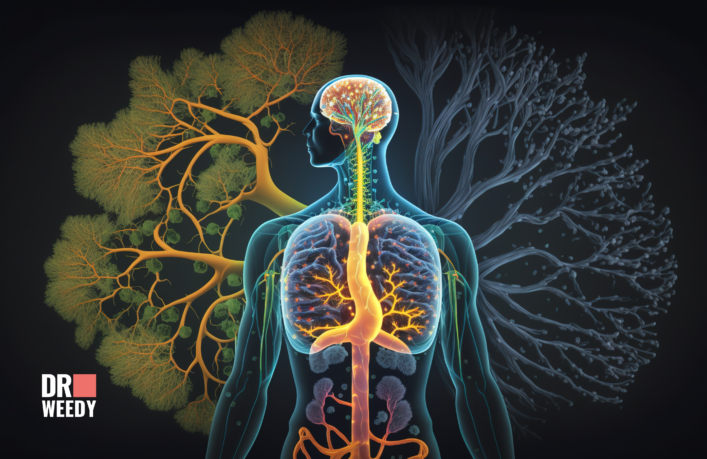
THC’s interaction with our bodies is not straightforward, but for ease of understanding, let’s break it down:
- Neurotransmitters: The messengers within us: Our nerve cells communicate using molecules called neurotransmitters, which transmit a variety of signals from the brain to different parts of the body (1). These neurotransmitters are vital in regulating our mood, appetite, sleep, and much more.
- Endocannabinoid System (ECS): The regulator: Our bodies have an endocannabinoid system (ECS) that plays a crucial role in maintaining our physiological homeostasis (2). The ECS produces its own cannabinoids (endocannabinoids) that interact with various receptors throughout the body, influencing the production and release of neurotransmitters.
- THC: The disruptor: THC resembles the structure of endocannabinoids and can therefore interact with the same receptors in the ECS (3). When THC binds to these receptors, it disrupts the normal functioning of the ECS, leading to an overproduction of certain neurotransmitters. This overproduction can lead to the ‘high’ associated with cannabis use, along with other effects on mood, perception, and physical sensations.
- Widespread Impact: Because the ECS is involved in a multitude of functions throughout our bodies, THC’s impact can be wide-ranging, affecting our central nervous system, immune responses, heart, and lungs (4).
Tips to Avoid Unpleasant Consequences of THC

Fortunately, there are simple tips that can help you navigate your THC consumption responsibly. By following these recommendations, you can enhance your cannabis experience and minimize any potential discomfort:
- Stay Hydrated: When consuming THC, it is important to drink plenty of water, even more than usual. Dehydration is a common side effect of THC overuse, and staying hydrated can help alleviate this issue.
- Find Your Preferred Consumption Method: Each individual has unique preferences when it comes to consuming cannabis. Experiment with different methods such as smoking, vaping, edibles, patches, or oils to determine what works best for you. Some individuals may not tolerate certain methods well, so finding the one that suits you can help prevent any unpleasant consequences.
- Start with Low-THC Strains: If you are new to using cannabis or have a low tolerance, it is advisable to begin with strains that have lower levels of THC. Gradually increase your dosage over time to avoid overwhelming effects. By taking it slow and steady, you can still have an enjoyable experience without feeling overwhelmed.
Additionally, consider exploring CBD-high strains that contain minimal amounts of THC. These strains, such as Elektra, Remedy, Harlequin, Pennywise, and others, offer the medicinal benefits of cannabis without the negative outcomes commonly associated with higher THC levels.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Cannabis Use
Cannabis can offer many benefits, but it’s essential to use it responsibly to avoid potential health risks. While some strains can provide a recreational “high,” it’s important to remember that these strains may also pose a greater risk of addiction and other side effects. Ultimately, the decision to use cannabis is a personal one, but it should be made with full awareness of the potential consequences. As with any substance, moderation and understanding are key to safe and beneficial use.
Sources:
- Neurotransmitters – Kenhub
- An introduction to the endogenous cannabinoid system – NCBI
- The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin
- Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System – NCBI


















Those that rate it low just are not willing to accept facts. REM sleep is also adversely affected by thc use. The THC crowd has been victimized by all the urban legend syndrome. Many read and accept that which supports their wishes rather than fact.
The living in fantasy and support for conspiracy are what we live in these days. Just like politics. Many believe anything that supports their viewpoint regardless the facts.