Is Marijuana A Depressant?

Although marijuana is one of the most widely used drugs in the world today many people are not well informed of its effects on the body. The cannabis plant has been cultivated for thousands of years, long before its legalization ship set sail, for its medicinal and psychoactive properties. It contains hundreds of different compounds, including THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), which is the main psychoactive ingredient, responsible for its complex effects on the brain.
So, in this article, we will discuss in detail whether marijuana can be classified as a depressant, how it operates in the body, and what to anticipate when using it.
What is a Depressant?
Drugs are categorized into different classes based on their primary effects on the central nervous system. These three basic classes include depressants, stimulants, and hallucinogens. It’s important to note that there are some drugs that exhibit characteristics of more than one class, blurring the lines between classifications—(marijuana is one of these).
Depressants are drugs that have the ability to slow down the CNS (central nervous system). As a part of their action, they induce relaxation, reduce anxiety, and promote sedation. Common examples of depressants include alcohol, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates.
Now, when cannabis is ingested, the two major compounds present in it (THC and CBD) will determine the effects that will be felt or experienced by the user. THC is the psychoactive compound in cannabis, which means it is responsible for the “high” feeling. While CBD, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and does not produce any intoxicating effects. Therefore, the ratio of THC to CBD in a cannabis product has a major impact on the effects it produces. For example, a product with a high THC content will produce a stronger high, while a product with a high CBD content may produce more therapeutic effects.
In addition to THC and CBD, other cannabinoids and terpenes present in cannabis can also influence its effects. On a general note, here is a summary of the main effects thought to be from THC and CBD:
Effects of THC
- Euphoria;
- Relaxation;
- Altered perception of time and space;
- Increased appetite;
- Drowsiness;
- Impaired cognitive function;
- Pain relief;
- Anti-inflammatory effects;
- Anxiolytic effects;
- Antipsychotic effects.
Effects of CBD
- Pain relief;
- Anti-inflammatory effects;
- Anticonvulsant effects;
- Anxiolytic effects;
- Antipsychotic effects;
- Improved memory and cognitive function;
- Reduced nausea and vomiting;
- Reduced anxiety and depression;
- Improved sleep quality.
So Is Cannabis a Depressant?
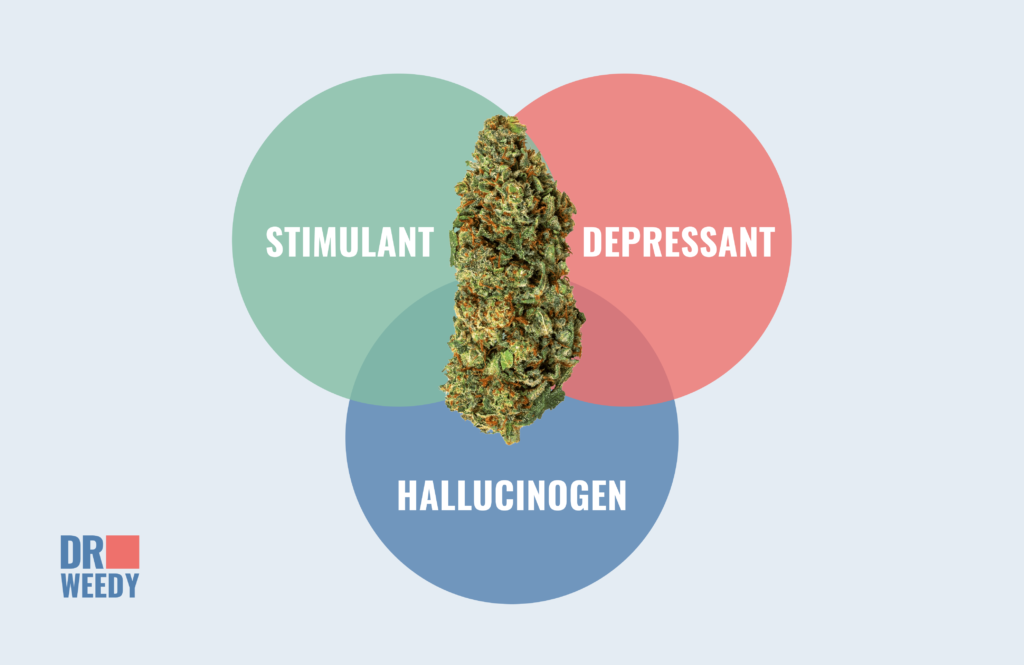

The answer is not as straightforward as it may seem. While marijuana is primarily known for its psychoactive properties and mood-altering effects, its classification as a depressant is quite complex. Marijuana does produce some depressant effects but it also possesses stimulating and hallucinogenic capabilities.
Studies have shown that marijuana can have sedative effects, inducing relaxation and calming anxiety when taken—-the normal mechanism of action of depressants. However, these effects are often dose and strain-dependent and can vary widely between individuals. This means that, when you ingest certain cannabis strains in the required dose, you may experience similar effects as those of traditional central nervous system depressants:
- Relaxation of the muscles and brain;
- Sedation;
- Reduced anxiety, etc.
Is Marijuana a Stimulant?
Marijuana has an interesting psychoactivity profile. It produces similar effects to CNS stimulants, especially during the initial phases of its use, primarily targeting and enhancing the activity of the central nervous system. The plant is known for increasing alertness and energy, as well as affecting concentration, and mood.
Like the depressant properties of cannabis, these effects can also vary according to the strain, chemical composition, and individual tolerance. Whatever the case, cannabis is known to produce one or more of the following stimulant-like properties:
- Increased Heart Rate;
- Elevated Mood;
- Enhanced Sensory Perception;
- Increased Energy;
- Improved Focus.
Weed finds its own way for each of us, working differently in different people. For some, it is a relaxant, for others — a stimulant or a hallucinogen.
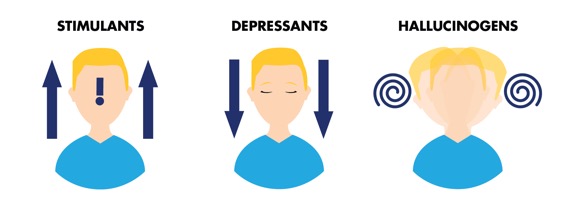
Is Marijuana a Hallucinogen?
Many people often assume that cannabis is capable of producing hallucinations; but the fact is that marijuana is not a classic hallucinogen, like LSD or psilocybin. Hallucinogens alter perception in a way that can cause people to see, hear, or feel things that are not really there. Marijuana can alter perception, but it does not typically cause hallucinations in the same way.
However, marijuana can cause some perceptual changes that are similar to those caused by hallucinogens. For example, marijuana can cause people to experience time distortion, changes in color and depth perception, and increased sensory awareness. In rare cases, marijuana can also cause hallucinations, but these are usually mild and short-lived.
Nevertheless, the likelihood of experiencing hallucinations from marijuana actually depends on a number of factors, including the dose, the strain of marijuana used, the method of consumption, and the individual user. Generally, people who are new to marijuana or who have a low tolerance for THC are more likely to experience hallucinations.
Benefits of Marijuana on Mental Health

Many patients diagnosed with various mental health conditions have reported relief and improvements in their symptoms since they started using medical marijuana. There are several positive effects of marijuana in managing mental health disorders.
1. Sleep Improvement
Sleep deprivation is deadly but as a result of work, business, and the demands of family, 60 to 70 million people in the world are suffering from different forms of sleep disorders.
The good news is that marijuana can help some people with sleep disorders, such as insomnia, to fall asleep faster and experience improved sleep quality. This is believed to be a result of THC’s ability to have sedative effects.
2. Pain Management
Marijuana has well-established analgesic properties, which can be beneficial for individuals with chronic pain conditions. It is believed that the interaction between the cannabinoids in marijuana and the endocannabinoid system in the body is responsible for this action. The endocannabinoid system helps regulate pain perception by modulating neurotransmitters in the brain and spinal cord.
3. Anxiety and Stress Reduction
Stress is a silent killer but it can be handled with a good strain of cannabis. Several individual reports and studies suggest reduced anxiety and stress levels after using marijuana, especially strains with higher CBD content. CBD exerts its anxiolytic effects by interacting with serotonin receptors in the brain, leading to reduced anxiety and stress.
4. Relief from Depression
Some individuals with depression have reported temporary relief from symptoms after using marijuana, which may be attributed to the interaction of certain cannabinoids, such as THC (delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol), with the endocannabinoid system. THC interacts with CB1 receptors in the brain, leading to temporary mood elevation and relaxation. A 2020 study found that marijuana provided rapid, short-term relief from depression symptoms for the vast majority of participants.
It is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of marijuana on mental health. However, the current evidence suggests that marijuana may be an effective adjunctive treatment for a variety of mental health conditions.
Can Marijuana Cause Depression?

There is no evidenced data that correlates weed with depression. What is known for sure is that there are people who regularly smoke weed and have depression. Yet, it is not known if cannabis is the factor that leads to this mental malady. Some say that due to its toxicity, weed can cause depression directly, affecting and damaging the brain. Others claim that marijuana is associated with depression and anxiety because its abuse leads to certain problems at work, school, and family.
More research is needed to better understand the relationship between marijuana use and depression. At the moment, it is simply assumed that marijuana can have both positive and negative effects on mood.
The Benefits of Responsible Marijuana Use

It’s essential to recognize that marijuana when used responsibly, can offer a range of benefits. Beyond its potential in managing mental health conditions, it can also improve social interactions, reduce stress, and stabilize mood.
Although dependent on dose and strain variety, marijuana can produce depressant, stimulant, and hallucinogenic properties. You must however take care at all times to avoid heavy marijuana consumption. Heavy marijuana consumption can lead to several negative consequences, including:
- Addiction;
- Cognitive impairment;
- Respiratory problems;
- Social and economic problems, etc
Final Thoughts
As we’ve seen in this article, marijuana is a drug with numerous compounds that act in different ways on the body. While it is not a classic depressant, it can produce some depressant effects, making its classification complex. It also has stimulant and hallucinogenic capabilities that vary according to the strain and chemical composition.
So if you are looking to enjoy the CNS depressant effects of marijuana, it is best to buy quality strains with the appropriate CBD:THC profile. Remember that it is always best to use marijuana responsibly and in moderation.
SOURCES:
- al’Absi M, Allen AM. Impact of Acute and Chronic Cannabis Use on Stress Response Regulation: Challenging the Belief That Cannabis Is an Effective Method for Coping. Front Psychol. 2021 Jul 1;12:687106. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.687106. PMID: 34276511; PMCID: PMC8283823.
- Barrett FS, Schlienz NJ, Lembeck N, Waqas M, Vandrey R. “Hallucinations” Following Acute Cannabis Dosing: A Case Report and Comparison to Other Hallucinogenic Drugs. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2018 Mar 1;3(1):85-93. doi: 10.1089/can.2017.0052. PMID: 29682608; PMCID: PMC5908416.
- García-Gutiérrez, M. S., Navarrete, F., Gasparyan, A., Austrich-Olivares, A., Sala, F., & Manzanares, J. (2020). Cannabidiol: A Potential New Alternative for the Treatment of Anxiety, Depression, and Psychotic Disorders. Biomolecules, 10(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111575
- Li X, Diviant JP, Stith SS, Brockelman F, Keeling K, Hall B, Vigil JM. The Effectiveness of Cannabis Flower for Immediate Relief from Symptoms of Depression. Yale J Biol Med. 2020 Jun 29;93(2):251-264. PMID: 32607086; PMCID: PMC7309674.
- Martin, E. L., Strickland, J. C., Schlienz, N. J., Munson, J., Jackson, H., Bonn-Miller, M. O., & Vandrey, R. (2021). Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of Medicinal Cannabis Use in an Observational Trial. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.729800
- Murray JB. Marijuana’s effects on human cognitive functions, psychomotor functions, and personality. J Gen Psychol. 1986 Jan;113(1):23-55. doi: 10.1080/00221309.1986.9710540. PMID: 3009708.
- NIDA. “What are marijuana’s effects?.” National Institute on Drug Abuse, 19 Apr. 2021, https://nida.nih.gov/publications/research-reports/marijuana/what-are-marijuana-effects
- Scherma, M., Muntoni, A. L., Riedel, G., Fratta, W., & Fadda, P. (2020). Cannabinoids and their therapeutic applications in mental disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 22(3), 271-279. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.3/pfadda