Endocannabinoid System & Cannabis

There is hardly a single person, especially among weed lovers, who has not heard or read an earful about the human endocannabinoid system (ESC for short) and its huge importance. The first-ever attempts to research the ECS were made in the 60s-70s of the past century. Scientists wanted to understand the mechanisms of cannabis to affect our bodies, and discovered that system. The research is still going on, but we already know that phytocannabinoids from weed co-work with our endogenous CBs, producing numerous healing and sometimes harmful effects.
What Is ECS And How It Works
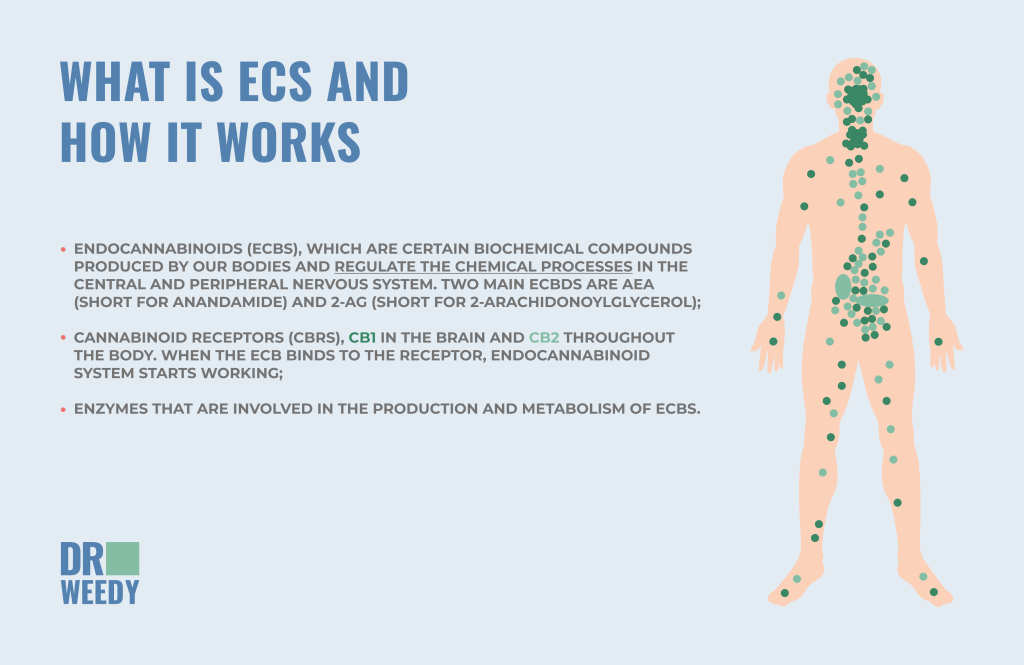
Endogenous cannabinoid system, or ECS, consists of three main components:
- endocannabinoids (eCBs), which are certain biochemical compounds produced by our bodies and regulate the chemical processes in the central and peripheral nervous system. Two main eCBDs are AEA (short for anandamide) and 2-AG (short for 2-arachidonoylglycerol);
- cannabinoid receptors (CBRs), CB1 in the brain and CB2 throughout the body. When the eCB binds to the receptor, endocannabinoid system starts working;
- enzymes that are involved in the production and metabolism of eCBs.
Depending on the endocannabinoid, receptor, and the body region, eCBs initiate numerous processes and produce multiple effects.
Endocannabinoid Mechanism In Layman’s Terms
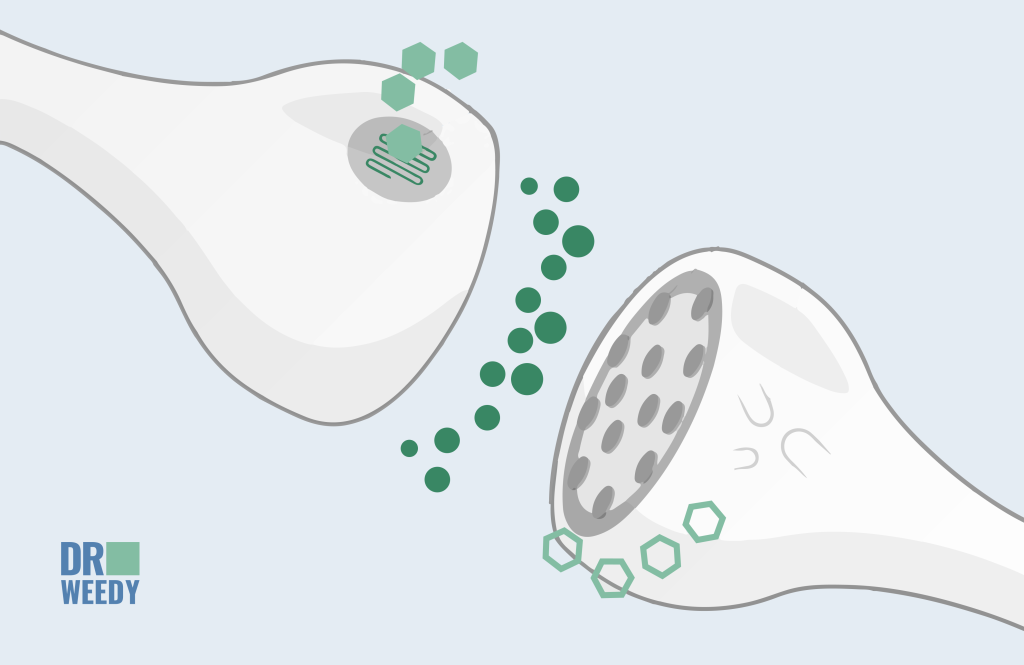
As it was already said, we still do not know all mechanisms and processes involved in the ECS functioning. However, we already know that eCBs are neuromodulators that provide steady and balanced functioning of the entire organism. Let’s try to understand this complex instrument:
- first of all, we need to mention neurotransmitters. These are the molecules in the nervous system and other organs released from one nerve cell to transmit the message or signal to another. This structure is called synapse;
- endocannabinoids downregulate the release of They go from the postsynaptic neuron to tell the presynaptic one to slow down or stop the production of dopamine, serotonin, noradrenaline, and others;
eCBs are produced only when they are needed, so they act as a kind of emergency flow control for our bodies and look after the healthy balance of the brain chemistry.
The Role Of Endocannabinoid System
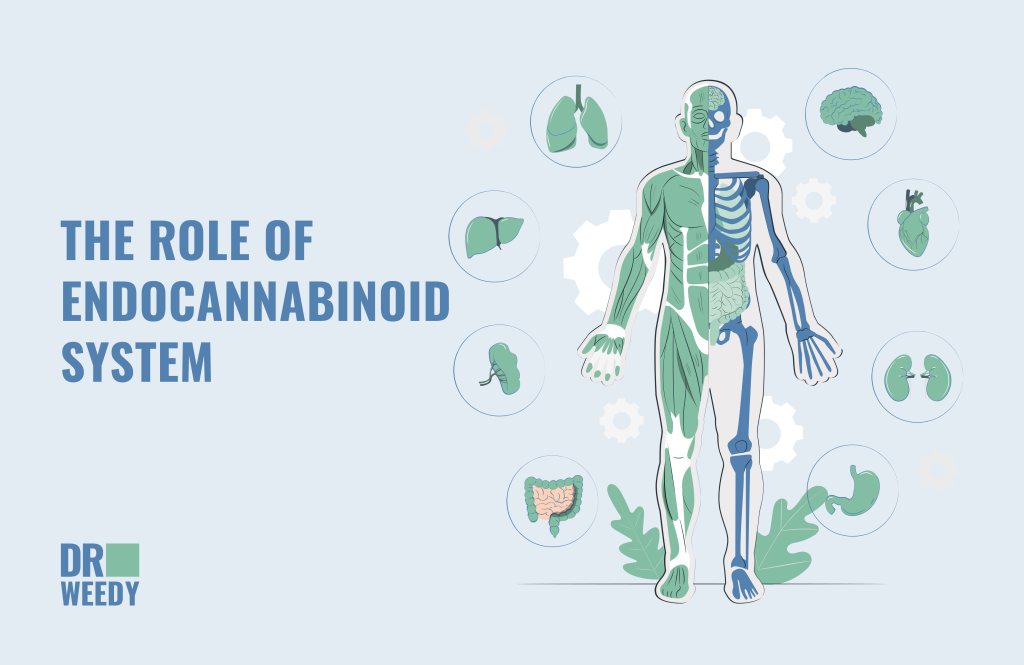
According to the latest research, endocannabinoid system takes part in the processes that influence numerous functions and conditions of our mental and physical health:
- cognitive functions and intellect;
- stress response;
- depression and anxiety;
- reward system and addictions;
- development and protections of nerve cells;
- sleep-wake cycle;
- liver health;
- insulin regulation;
- fertility;
- heart and vessels ailments;
- bone formation;
- energy balance;
- motor control;
- immune response;
- digestion, nausea, appetite disorders;
- malignant tumors.
There is a clinically diagnosed condition that occurs when our body does not produce enough eCBs, it is called clinical endocannabinoid deficiency syndrome, or CEDS. The list of health problems associated with this malady is impressive:
- mood and psychiatric disorders;
- migraines;
- fibromialgia;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s;
- inflammations;
- substance addictions;
- chronic stress;
- psoriasis, etc.
This list is not final, the number of CEDS-induced diseases is much higher, and the studies are still going on.
ECS and THC

When we smoke THC-high weed, this active ingredient of cannabis quickly attacks CBRs and blocks them from binding to our natural cannabinoids. As a result, the presynaptic neurons do not receive the signal to slow down and keep producing neurotransmitters. This inevitably leads to disbalance all throughout the body. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) binds to CR1 and CR2, and affects the functioning of all systems. Here are the signs of the THC overdose:
- slowed reaction;
- anxiety;
- panic attacks;
- memory and cognitive impairments;
- euphoria;
- impaired perception;
- hallucinations;
- disorientation, etc.
There are also positive effects of THC, first of all its pain-relieving and sleep-improving potencies.
Endocannabinoid System and CBD
CBD (short for cannabidiol) is the second main cannabis active chemical compound. Administration of CBD can be very helpful in patients with the endocannabinoid deficiency and other ailments. The cooperation of the endocannabinoid system and CBD is indirect, it does not bind to the CBRs. Instead, it works in different body regions with various systems and receptors. But its main activities are directed to support and assist the performance of ECS.

Benefits of Medical Cannabis
Here are some of the health-improving effects of cannabidiol:
- CBD activates TRPV1 receptors that are responsible for pain, inflammation, and body temperature. These receptors normally are activated by AEA, thus CBD helps our ECS perform its functions;
- CBD slows down the action of the enzyme that breaks down endogenous cannabinoids;
- it binds to dopamine receptors, thus combating depression and increasing cognitive abilities and motivation;
- opioid receptors also interact with CBD, which makes it an effective analgesic;
- it activates serotonin, thus fighting anxiety, addictions, mood disorders;
- there is a type of receptors, GPR55, that were found to be associated with seizures and epilepsy. CBD inhibits the action of GPR55;
- glycine receptors also co-work with CBD, which is how it acts as an effective anti-inflammatory and analgesic drug.
Moreover, CBD appears to be the antagonist for THC. This is another example of the indirect action of CBD — it does not let THC molecules to bind to the CB1 and alleviates the adverse effects of cannabis abuse.

Conclusion
Hopefully, this article helped you understand what is the endocannabinoid system and how it works. As you can see, medical marijuana is a powerful remedy for many health conditions, because it contains lots of CBD and almost zero THC. The former has no negative side effects, and it does not affect our ECS directly, but it facilitates its performance and helps us keep up the normal level of eCBs. With the help of CBD-high weed, you will keep your body in balance and prevent many mental and physical health problems.