Marijuana’s Role in Alleviating Multiple Sclerosis Symptoms

Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a debilitating and chronic disease that affects over 1.8 million people worldwide. Its symptoms can cause significant discomfort to those who suffer from it. Although there are medications for managing most symptoms associated with the disease, they often come with a range of disturbing side effects. However, research suggests that marijuana may be beneficial in alleviating some of the symptoms associated with MS. So in this article, we will explore the potential benefits of managing MS symptoms with cannabis and how to use it right.
What is Multiple Sclerosis?
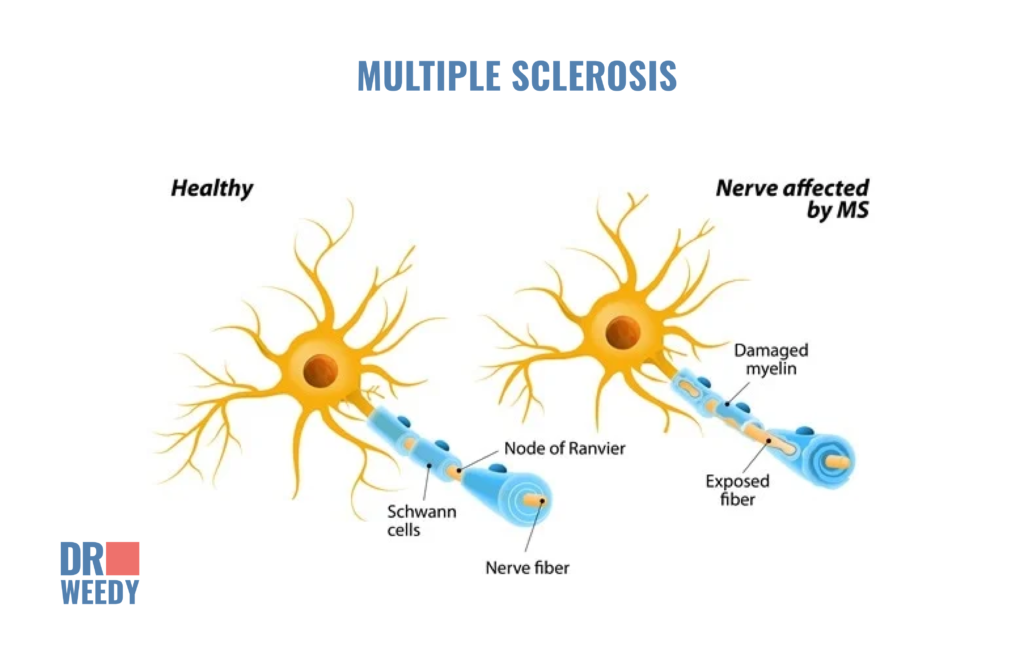
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS), which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The exact cause of multiple sclerosis is unknown, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disease, in which the immune system attacks the myelin sheath (the protective coating that surrounds nerve fibers) of the nervous system. This damage disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses along the nerves, resulting in a variety of physical and cognitive impairments.
Multiple sclerosis is non-contagious. Although it is most commonly diagnosed in people between the ages of 20 and 50, it can occur at any age. Studies have shown that women are more likely to develop MS than men. Nevertheless, there are a range of predisposing factors that may play a role in the development of MS including vitamin D deficiency, obesity, smoking, and genetics.
What Are the Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis?
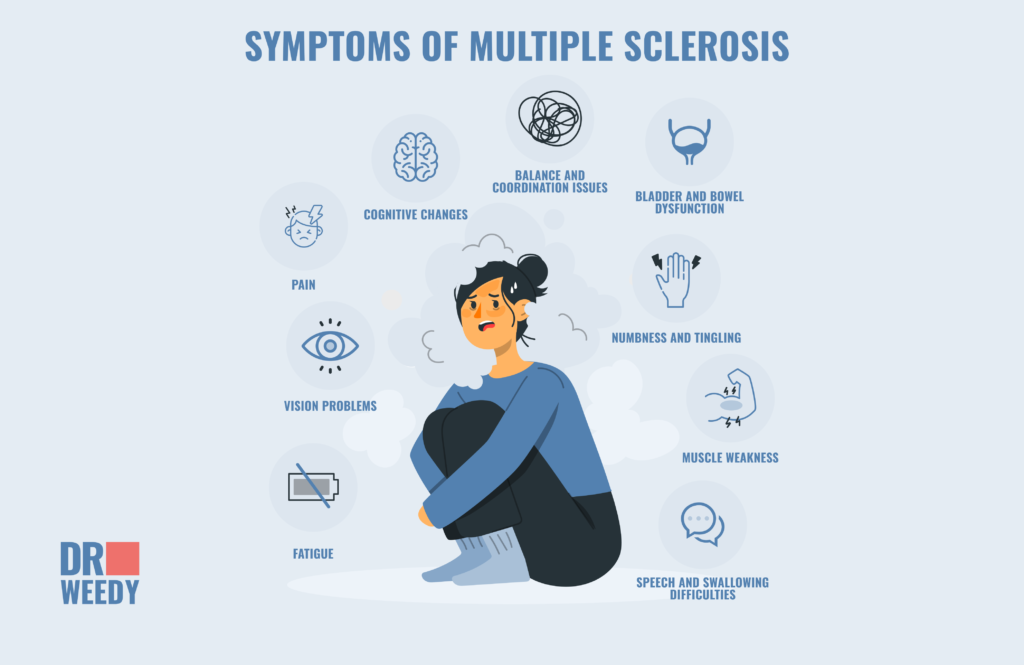
Multiple Sclerosis is associated with a variety of symptoms including the following:
- Fatigue: This is perhaps one of the most common symptoms of MS. The extreme tiredness can be persistent and overwhelming, significantly impacting a person’s daily life. Patients often describe it as relentless exhaustion that can make daily activities challenging.
- Numbness and Tingling: As a result of the damage to nerve fibers many individuals with multiple sclerosis experience numbness or tingling sensations, often in the extremities.
- Muscle Weakness: Muscle weakness can affect various muscle groups, leading to difficulties with walking, lifting objects, or performing everyday tasks.
- Vision Problems: Vision problems, such as blurred vision, double vision, or partial loss of vision, can occur when MS affects the optic nerve.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: People with MS may experience problems with balance and coordination, making it challenging to walk and maintain stability.
- Pain: Chronic pain is a common symptom of MS, affecting the muscles, joints, or even the face (trigeminal neuralgia). It may also manifest as neuropathic pain, with a burning or tingling sensation.
- Cognitive Changes: Cognitive impairment, including memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and mood changes, can be observed in individuals with MS.
- Speech and Swallowing Difficulties: In some persons, MS may affect the muscles responsible for speech and swallowing, leading to slurred speech or difficulties.
- Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction: MS can lead to issues with bladder control, causing urinary urgency, frequency, or incontinence. Bowel problems can also occur.
Is Marijuana an Effective Treatment for Multiple Sclerosis?

The main reason behind the wave of medical marijuana legalization in the US is its robust medicinal potency, offering relief to those for whom traditional orthodox medicine has proven ineffective.
Millions of people worldwide now enjoy an improved quality of life thanks to CBD and medical marijuana. The evidence is so compelling that CNN’s Chief Medical Correspondent, Dr. Sanjay Gupta, who once opposed medical marijuana, became a staunch advocate for its medicinal use after thorough research and witnessing its transformative impact on patients.
Marijuana’s therapeutic mechanism in treating multiple sclerosis lies in its various compounds, including delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), which interact with the human body’s endocannabinoid system. This interaction enables cannabis to deliver relief and wellness to its users..
How Can Marijuana Help in Multiple Sclerosis?

Marijuana can help those with multiple sclerosis in the following ways:
1. Reduction of Muscle Stiffness
Muscle stiffness results in lots of discomfort. Although there are several drugs for managing it, they often result in some unwanted side effects such as weakness. However, studies have shown that cannabis can effectively reduce stiffness associated with multiple sclerosis.
A 2012 study in the UK found that an oral extract of cannabis was more effective than a placebo in reducing muscle stiffness in people with MS. The extract was taken from Cannabis sativa L and the main cannabinoid was THC.
2. Reduced Muscle Spasticity
Moderate evidence suggests that cannabis can be effective in reducing muscle spasticity in people with multiple sclerosis. This 2010 analysis of three studies found that nabiximol (Sativex), a mouth spray containing cannabinoids, reduced people with MS’s self-reported spasticity.
3. Pain Management
Cannabidiol (CBD), a compound found in cannabis, is a very potent analgesic that is effective in managing chronic pain. They can reduce neuropathic pain and improve the overall quality of life for MS patients.
4. Improved Bladder Control
If you are experiencing neurogenic bladder symptoms, such as urge incontinence, nocturia, or urinary frequency you may find help in cannabis. Marijuana extracts have been found to be effective in improving some refractory neurogenic symptoms in patients with multiple sclerosis. This includes reducing episodes of urge incontinence, reducing nocturia, and improving bladder control.
5. Improved Sleep
Many MS patients struggle with sleep disturbances. However, marijuana can have a calming effect on the mind and body, promoting better sleep and reducing insomnia.
6. Anti-Inflammation
Inflammation can quickly destroy other organs and tissues of the body, exacerbating the progression of multiple sclerosis. The effectiveness of cannabinoids as strong anti-inflammatory agents is attributed to their ability to induce apoptosis, inhibit cell proliferation, suppress cytokine production, and promote the generation of T-cells. It is also believed to protect the brain cells from damage.
7. Appetite Stimulation
Loss of appetite is a common issue for individuals with MS, often resulting from nausea and gastrointestinal problems. Marijuana can stimulate the appetite, due to the presence of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), helping patients maintain a healthy weight and overall well-being.
Is Multiple Sclerosis a Lifelong Condition?
The short answer is, yes, MS is a lifelong condition. There is currently no cure for the disease. However, the course of MS can be highly variable, and individuals experience it differently. There are different types of MS, which can influence the disease’s trajectory. The most common types include:
- Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS): This is characterized by periods of relapses (worsening of symptoms) followed by periods of remission (recovery).
- Primary Progressive MS (PPMS): In this form, symptoms steadily worsen from the beginning, with no remission periods.
- Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS): Many individuals with RRMS eventually transition to SPMS, where there is a steady worsening of symptoms, with or without relapses.
- Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS): CIS represents the first occurrence of neurologic symptoms due to central nervous system inflammation and demyelination.
How to Use Marijuana in Alleviating Multiple Sclerosis

While marijuana may offer potential benefits for managing Multiple Sclerosis, it’s essential to use it safely and responsibly.
- Get Your MMJ Card with Ease: Dr. Weedy offers competitive rates for obtaining your medical marijuana card through our licensed and experienced physicians in all states that have legalized medical cannabis.
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Before incorporating marijuana into your treatment plan, you should consult with your healthcare provider for guidance and advice.
- Start Low and Go Slow: If you’re new to using marijuana, start with a low dose and gradually increase it until you achieve the desired symptom relief.
- Choose the Right Strain: Different strains of marijuana have varying ratios of THC and CBD. Choose the best strains for your needs.
Final Thoughts
Although there is no known cure for multiple sclerosis, the use of marijuana as a complementary treatment can significantly relieve some of its symptoms and enhance the quality of life of people living with MS.
While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing the symptoms, a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support can make a significant difference. If you or someone you know is considering including marijuana or CBD in multiple sclerosis treatment, it is important to first consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
SOURCES:
- Bains S, Mukhdomi T. Medicinal Cannabis for Treatment of Chronic Pain. [Updated 2022 Dec 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574562/
- Haddad, F., Dokmak, G., & Karaman, R. (2022). The Efficacy of Cannabis on Multiple Sclerosis-Related Symptoms. Life, 12(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/life12050682
- Mack A, Joy J. Marijuana as Medicine? The Science Beyond the Controversy. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2000. 7, MARIJUANA AND MUSCLE SPASTICITY. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK224382/
- Cannabis (Marijuana) and Cannabinoids: What You Need To Know. (2018). Retrieved October 17, 2023, from NCCIH website: https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know
- Zajicek JP, Hobart JC, Slade A, et al. Multiple Sclerosis and Extract of Cannabis: results of the MUSEC trial. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2012;83:1125-1132.
- Zhu, S., Wang, Z., Tao, Z., Wang, S., & Wang, Z. (2022). Relationship Between Marijuana Use and Overactive Bladder (OAB): A Cross-Sectional Research of NHANES 2005 to 2018. The American Journal of Medicine, 136(1), 72-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2022.08.031






